Market Movers: Targa’s $1.25B acquisition of Stakeholder Midstream deepens its northern Delaware Basin footprint, adds underutilized gas processing and NGL optionality to support Speedway, and intensifies competitive pressure on Permian NGL takeaway systems.
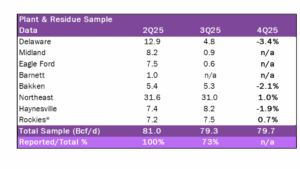
Estimated Quarterly Volumes: Delaware (-3.4%), Bakken (-2.1%) and Haynesville (-1.9%) volumes are trending down while Northeast (1.0%) and Rockies (0.7%) volumes are trending up Q-o-Q.
Calendar: EDA will be in Houston from Jan. 12-16. Financial models will be updated on Jan. 16. Texas plant data will be updated by Dec. 29.
Market Movers:
Targa Resources (TRGP) is doubling down on the northern Delaware Basin. On Dec. 1, the company announced it will acquire Stakeholder Midstream for $1.25B. The price represents ~6x estimated unlevered FCF in 2026.
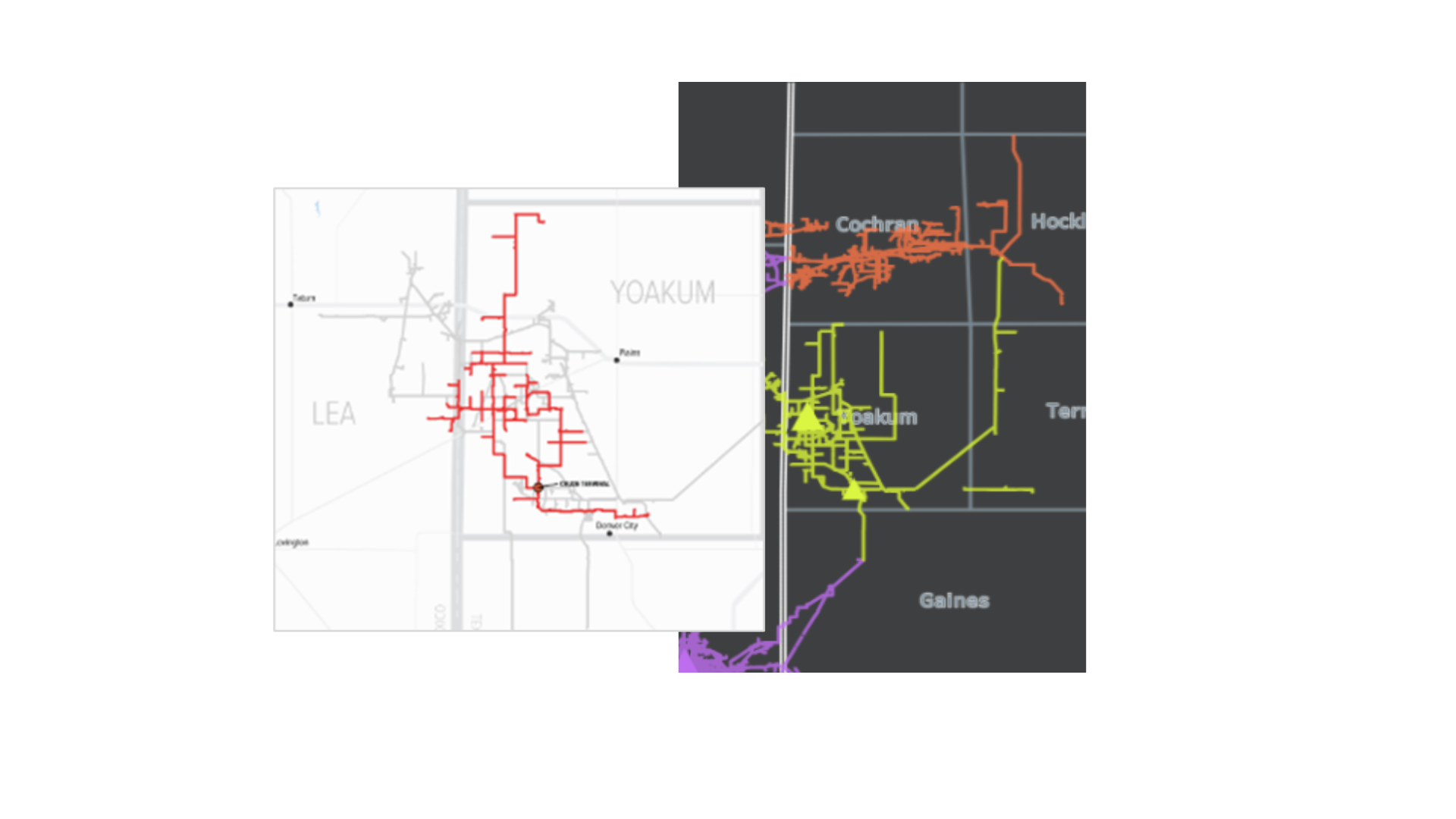
The Stakeholder deal will add about 460 miles of low-pressure gathering pipe and ~180 MMcf/d of processing capacity across Yoakum and Gaines counties, TX and Lea County, NM. Stakeholder also brings sour gas treating capability, a small crude gathering system, and carbon-capture operations that qualify for federal 45Q tax credits.
Details on the private Stakeholder assets and counterparties are available in the “G&P System Analysis” dashboard in Energy Data Studio. The top producers on the system include Burk Royalty, Hilcorp and Ring Energy.
Stakeholder’s primary strategic value for TRGP is its gas G&P footprint. Stakeholder’s Campo Viejo gathering system (shown in yellow in the map) includes two gas processing plants currently running at around 60% utilization. The assets are contiguous to Targa’s own G&P systems in the Delaware (shown in purple and red in the map), and the spare processing capacity gives TRGP meaningful operating leverage to capture future growth and optimize flows across its Permian network.

East Daley’s latest plant inlet data shows the Stakeholder system producing ~15 Mb/d of NGLs. Once TRGP builds the necessary interconnects, these barrels could help fill its recently announced Speedway system, tightening the race for NGL supply in the Permian.
Any change in flows would likely depend on contracts expiring. But a rerouting of Stakeholder barrels would apply pressure to competing pipelines, including Enterprise Products’ (EPD) Seminole and Chaparral pipelines and ONEOK’s West Texas LPG. The systems all interconnect with Stakeholder plants and already face competition for Permian NGLs. TRGP’s acquisition of Stakeholder adds another headwind.
The deal also creates optionality for TRGP to monetize non-core pieces like Stakeholder’s San Andres crude gathering network (see figure). TRGP has demonstrated an interest in extracting value from peripheral assets, such as its 2019 sale to Blackstone of a 45% interest in its Badlands asset in North Dakota. The company could revisit divestitures if leverage begins to drift toward the upper end of its target range.

The Permian Basin at a Crossroads: Download Why This Pipeline Boom is Different
The Permian’s next big buildout is already taking shape — but this time, the drivers aren’t producers chasing oil. East Daley’s latest white paper reveals how gas demand from AI data centers, LNG exports, and utilities is rewriting the midstream playbook. Over 9 Bcf/d of new capacity and $12 billion in investments are reshaping flows, turning the Permian into a gas powerhouse even as rigs decline. Read Part II: Why This Pipeline Boom is Different
Investor takeaway: The Stakeholder acquisition enhances TRGP’s Permian optionality, positions Speedway for higher throughput, and heightens NGL barrel competition — potentially altering flows across multiple long-haul systems.
Estimated Quarterly Volumes:
Notes:
Total Sample represents the flow sample and plant data accessible to EDA. The latest Q-o-Q percentage change is estimated by comparing either flow sample data Q-o-Q or plants within a basin that have contiguously reported inlet volumes from the prior quarter to the current quarter. Sample data is now inclusive of all plant data within a basin, resulting in a one-time change to total sample basin levels in 2Q and 3Q. 4Q25 is expressed as Q-o-Q growth from 3Q25.
Rockies represents the aggregate of Big Horn, DJ, Green River, Piceance, Powder River, San Juan, Uinta and Wind River basins.
- Delaware: Delaware plant inlet data is down 3.4% from 3Q25 based on October data. ET–CEQP Sendero Midstream is down 12.2% while KNTK–Durango Midstream is up 8.6%. The largest producer on the Kinetik system is Mewbourne Oil, accounting for ~40% of production.
- Northeast: Northeast flow sample data is up 1% from 3Q25 based on the latest data. HG Midstream’s dry gas volumes are down 11.8% and DTM–AGS volumes are up 16.0%. The largest producer on the DTM system is Northeast Natural Energy, accounting for ~80% of production.
Calendar: